Weaker-than-expected macroeconomicsituationcontinuedto weigh on TSMC’sQ2 2023 business performance.温和smartphone and PC/NB demand negatively impactedtheoverall utilization rateduring the quarter.Though largely expected by the market, the company further cut its full–year revenue guidance ontheweaker end demandexpected forH2 2023.However,TSMCprojects astrong AI demand inQ32023and,going forward,sees itself asthe key enablerfor AI GPUsandASICs that requirealarge diesize.We give ourtakeson the key points discussed during theearnings call:
Is AI semiconductor demand real?
- Chairman(Mark Liu):我们不能预测不久的将来,意思不xt year, how the sudden demand will continue or will flatten out. However, our model is based on the data center structure. We assume a certain percentage of the data center processors areAIprocessors and based on that, we calculate the AI processor demand. And this model is yet to be fitted to the practical data later on. But in general, I think the trend of a big portion of data center processors will be AI processors is a sure thing. And will it cannibalize the data center processors? In the short term, when thecapexof the cloud service providers is fixed, yes, it will. It is. But as for the long term, when their data service – when the cloud services have the generative AI service revenue, I think they will increase the capex. That should be consistent with the long-term AI processor demand. And I mean the capex will increase because of the generative AI services.
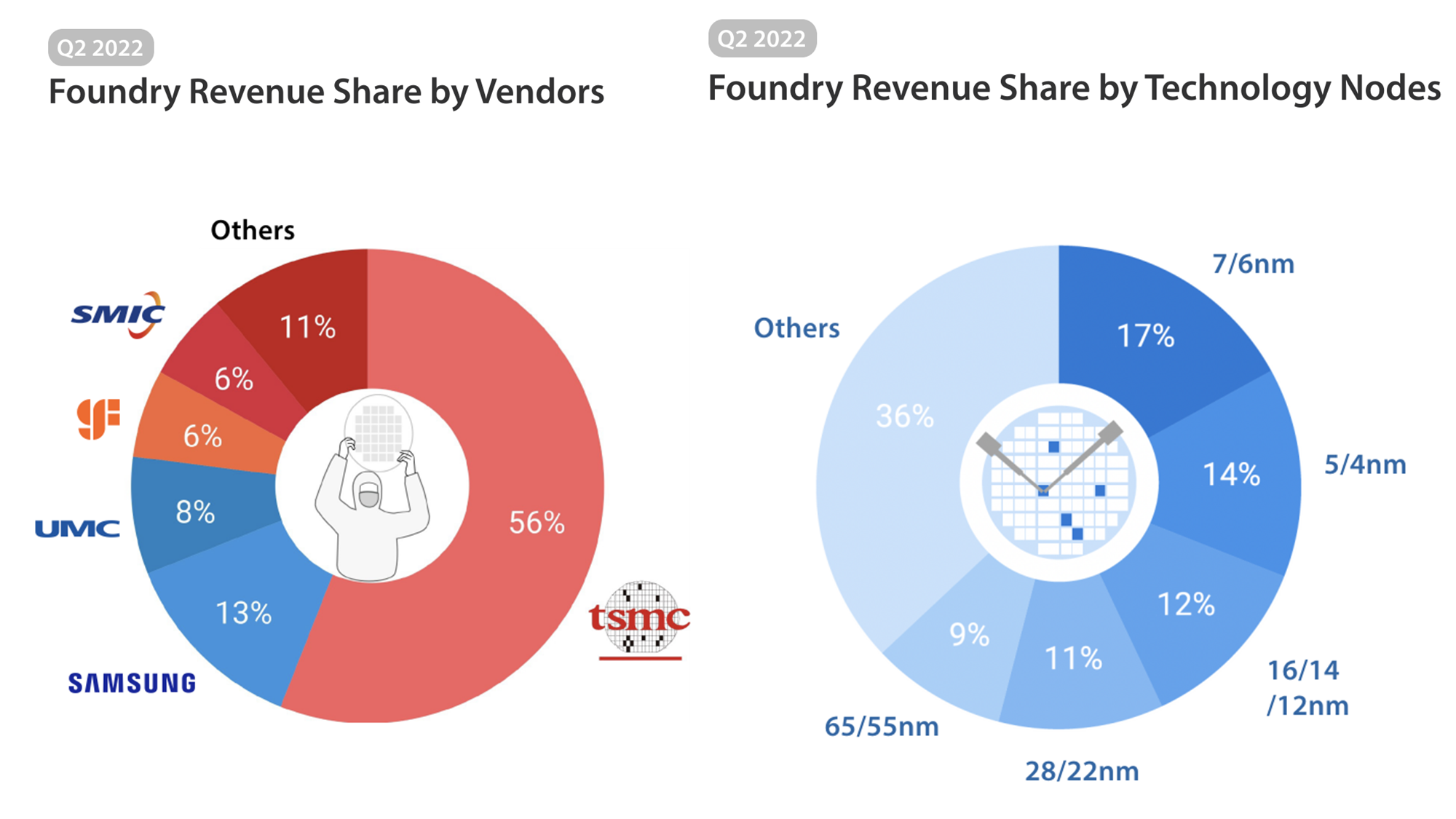
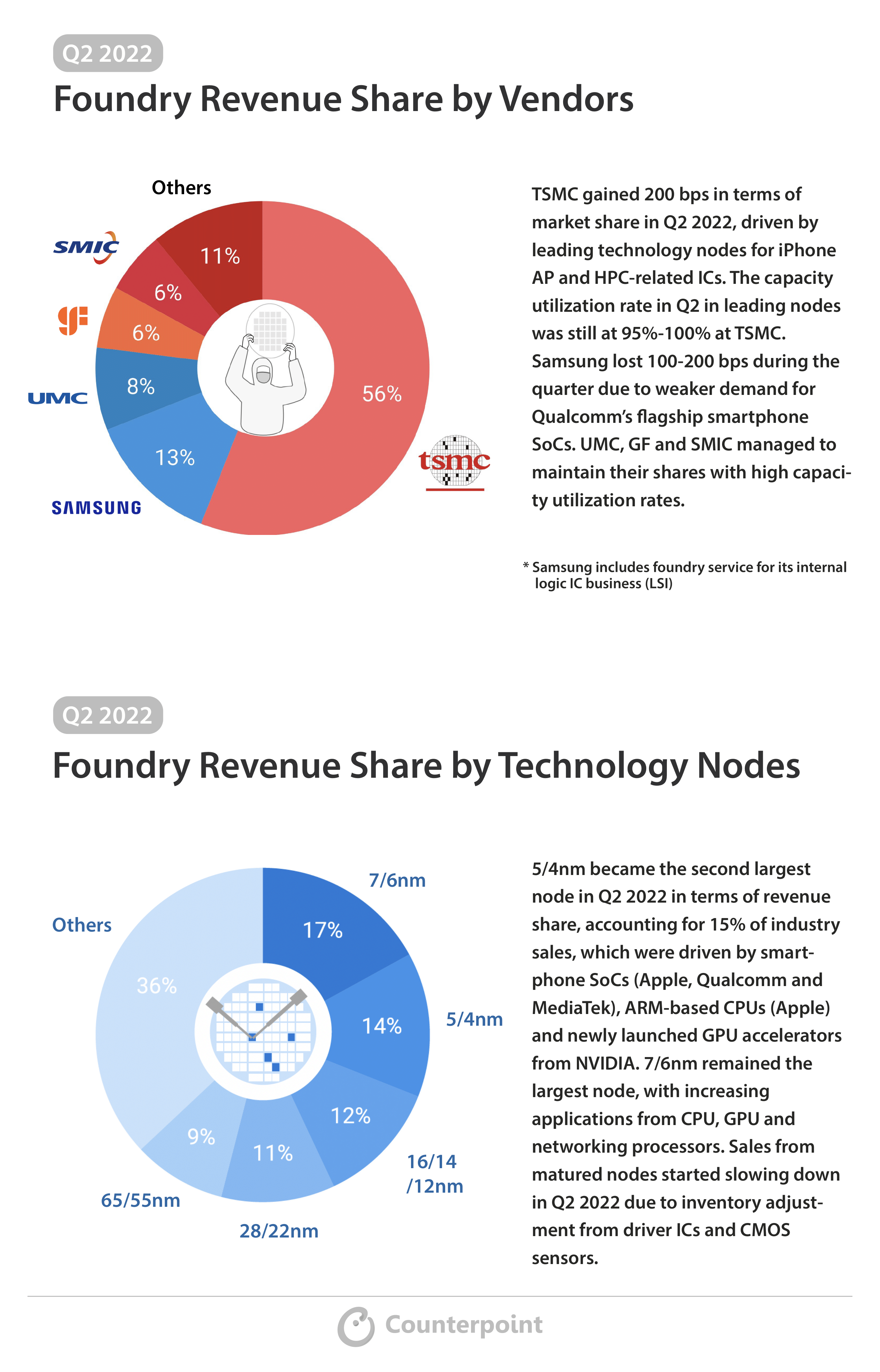
- Adam Chang’sanalyst take:Supply chain checks reveal that cloud service providers such as Microsoft, Google, and Amazon aggressively invest in AI servers.NVIDIAis continuing to add orders for the A100 and H100 to the supply chain, echoing the strong momentum for AI demand. TSMC holds a significant market share in AI semiconductorwaferproduction, mitigating the risk of misjudging CoWoS capacity expansion concerning AI demand.
- Akshara Bassi’s analyst take:Over the medium term, as hyperscalers continue to develop their own proprietary AI models and look to monetize through AI-as-a-Service and simiilar models, the infrastructure demand should remain robust.
Can AI semiconductor demand offset short-term macro weakness?
- CEO (Che-Chia Wei):三个月前,我们可能更乐观, but now it’s not. Also, for example, China economy’s recovery is actually also weaker than we thought. And so, the end market demand actually did not grow as we expected. So put all together, even if we have a very good AIprocessordemand, it’s still not enough to offset all those kinds of macro impacts. So, now we expect the whole year will be -10% YoY.
- Adam Chang’s analyst take:Although there is a lot of promise around AI, it would only account for around 6% of total revenues in 2023. Therefore,AIis not a panacea for broader short-term demand weakness.
Is TSMC CoWoScapacity enough to fulfill current AI demand?
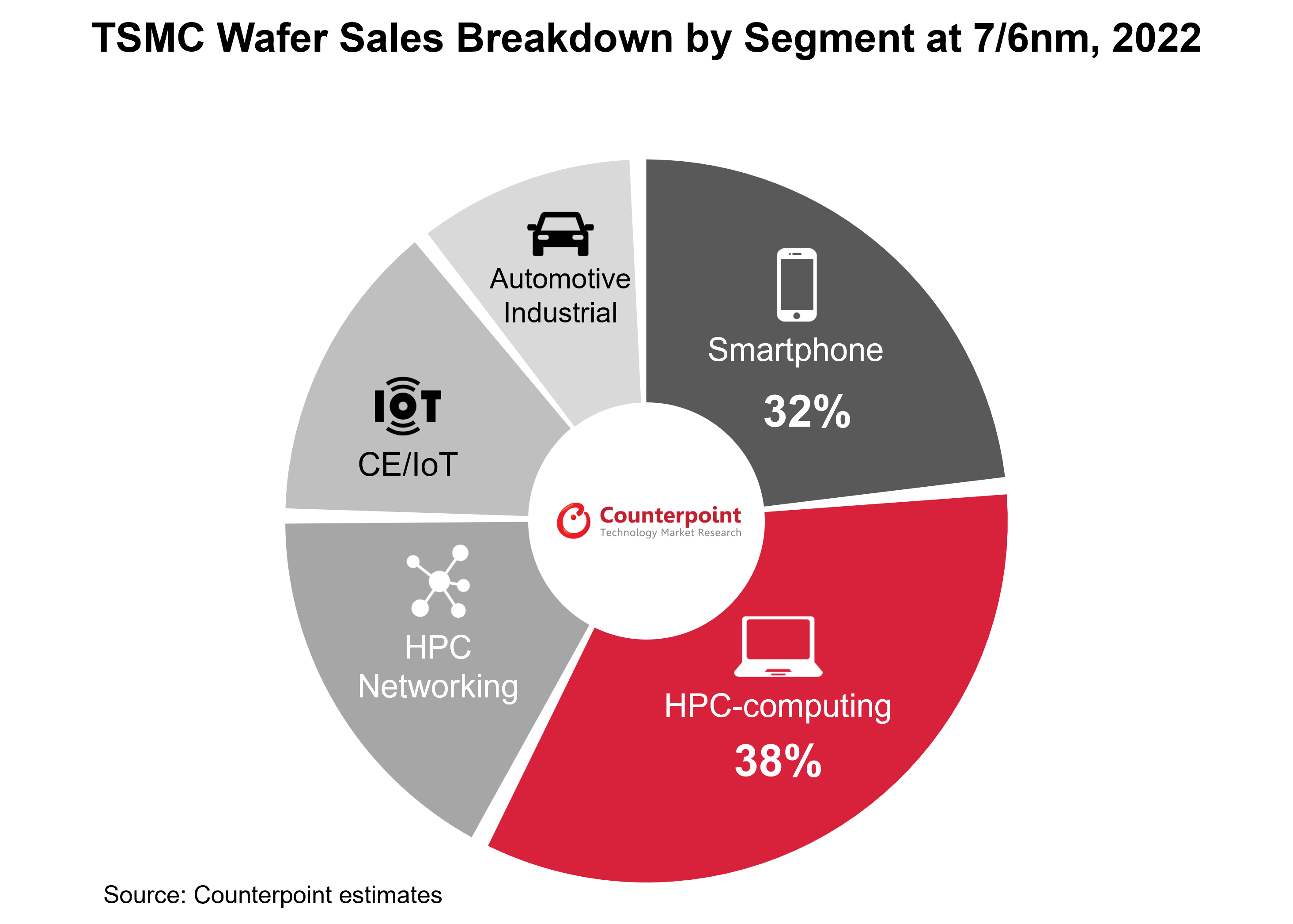
- CEO (Che-Chia Wei):For AI, right now, we see very strong demand, yes. For the front-end part, we don’t have any problem to support, but for the back end, the advanced packaging side, especially for the CoWoS, we do have some very tight capacity to — very hard to fulfill 100% of what customers needed. So, we are working with customers for the short term to help them to fulfill the demand, but we are increasing our capacity as quickly as possible. And we expect these tightening will be released next year, probably toward the end of next year. Roughly probably 2x of the capacity will be added.
- Adam Chang’s analyst take:Due to TSMC’s CoWoS capacity constraints, the company is finding it challenging to fulfill the strong AI demand from customers,, including NVIDIA,Broadcom, and Xilinx, at the moment. NVIDIA is actively seeking second- source suppliers asTSMClooks to outsource some of its production.
N3E/N3/N2 status
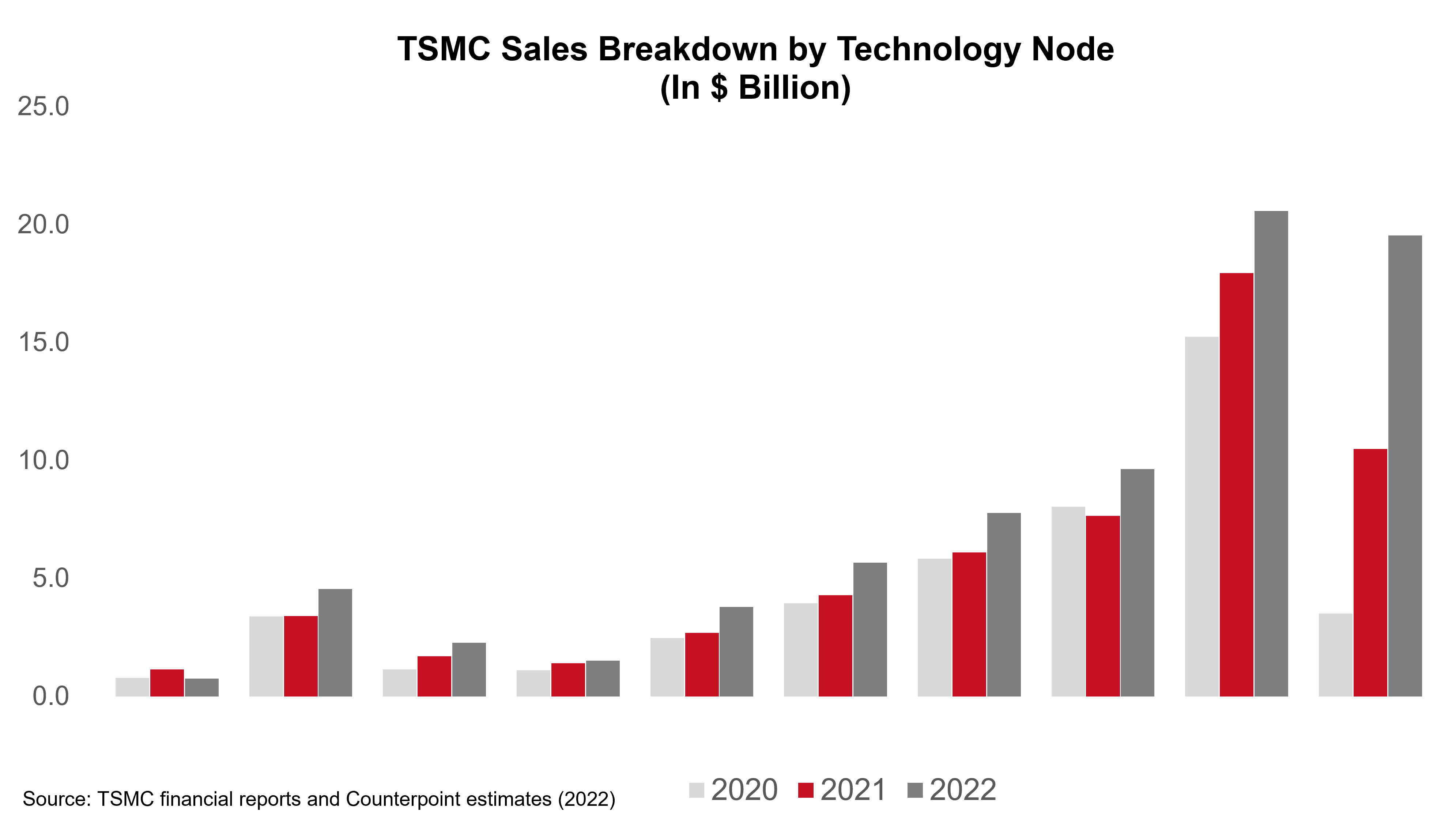
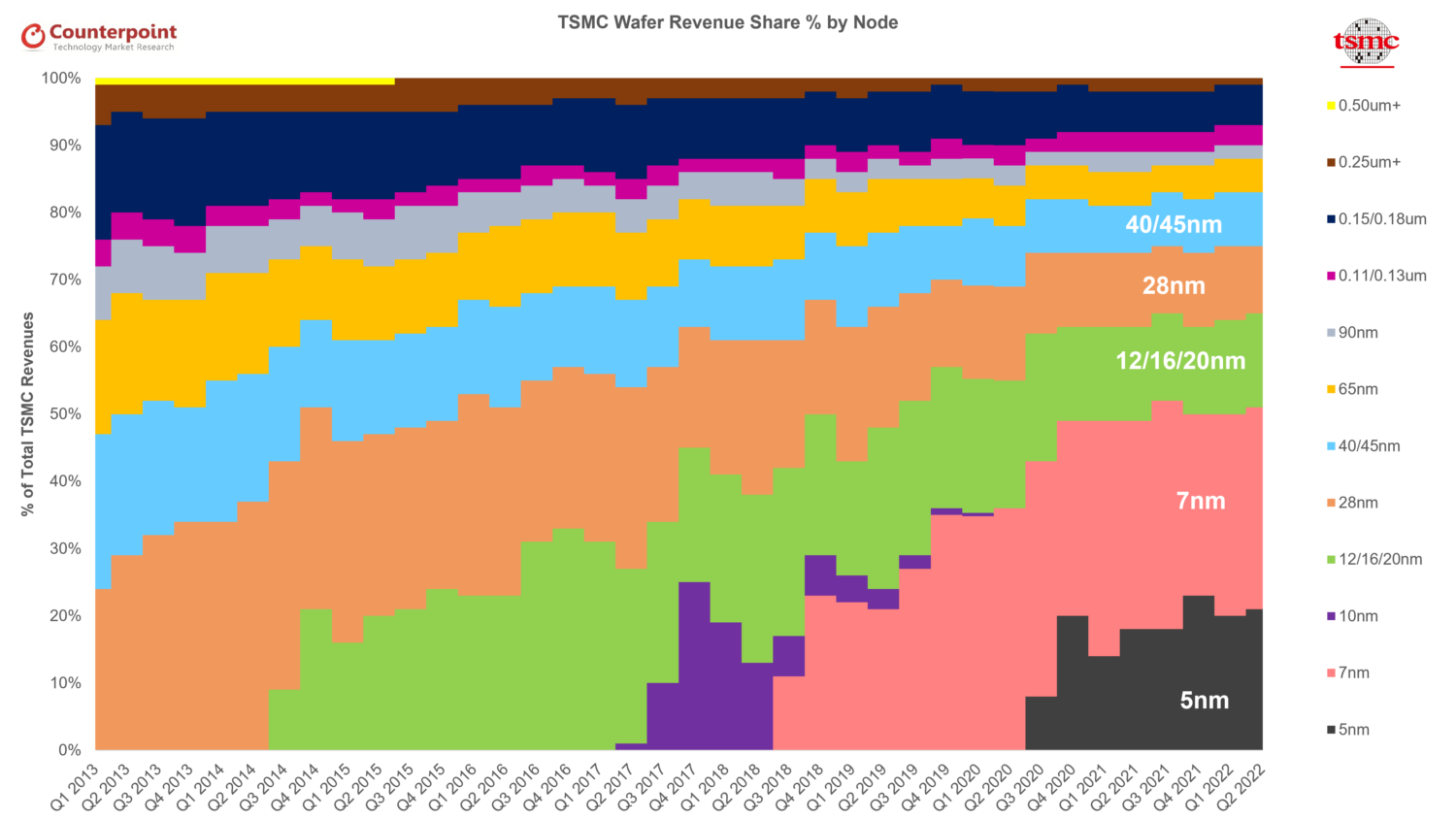
- CEO (Che-Chia Wei):N3 is already involved in production with good yield. We are seeing robust demand for N3 and we expect a strong ramp in the second half of this year, supported by both HPC and smartphone applications. N3 is expected to continue to contribute mid-single-digit percentage of our total wafer revenue in 2023. Our N2 technology development is progressing well and is on track for volume production in 2025. Our N2 will adopt a narrow sheet transistor structure to provide our customers with the best performance, cost, and technology maturity.
- Adam Chang’s analyst take:Apple is the sole customer expected to adopt TSMC’s 3nm technology in its A17 Bionic and M3 chips during 2023. TheQualcommSnapdragon 8 Gen 4 processor is also anticipated to join the TSMC 3nm family (N3E) in 2024. Moreover, Intel is likely to adopt TSMC’s 3nm technology for its Arrow LakeCPU, scheduled to launch in H2 2024.

Results summary
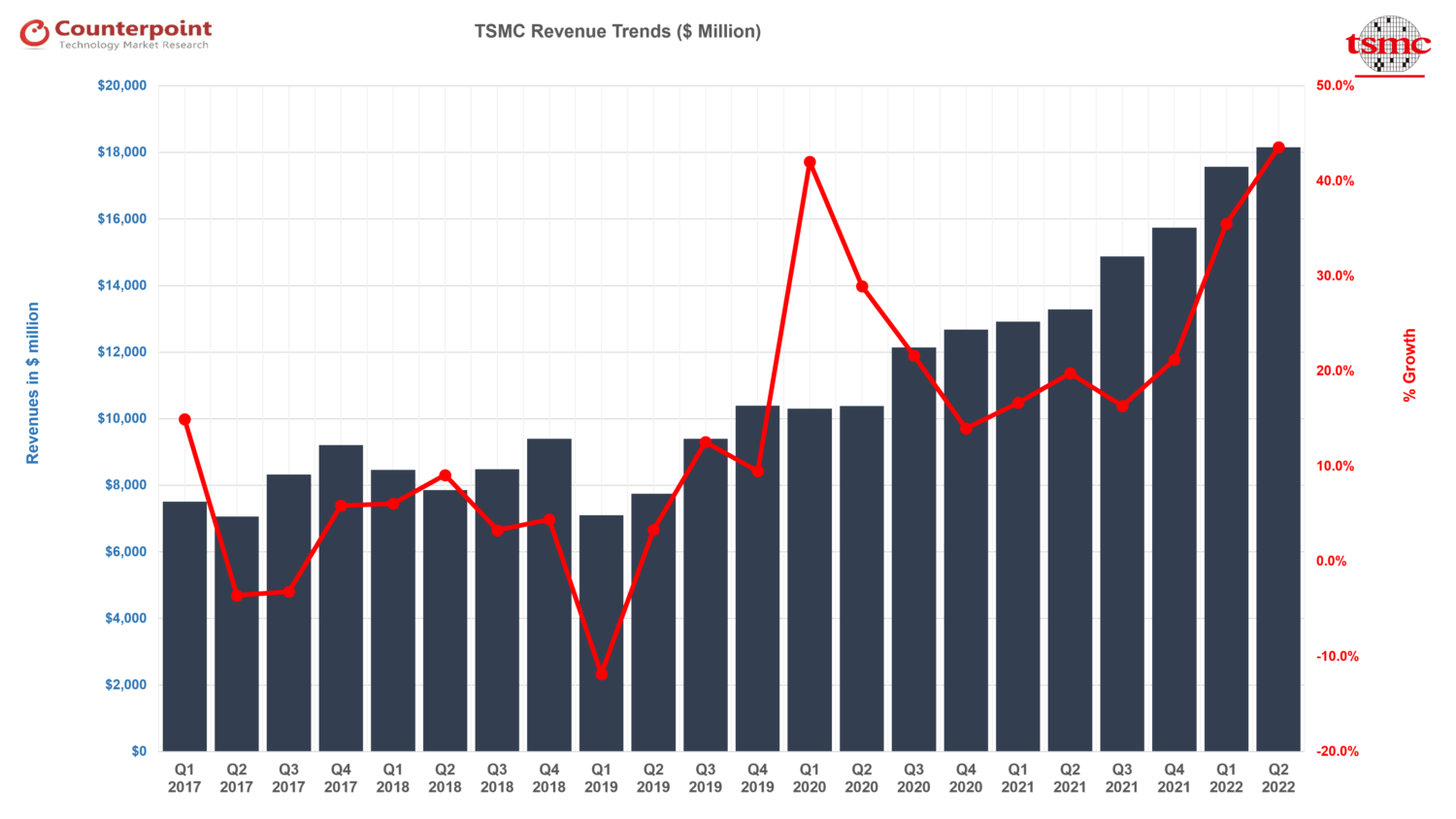
- Q2 2023resultsbeatslightly:TSMC reported $15.67 billion in sales, slightly above the midpoint of guidance. EPS beat consensus due to higher non-operating income. Both GPM and OPM slightly beat guidance thanks to favorable FX and cost control efforts.
- Q3 2023guidance in line:The management guided $16.7-$5 billion (+9% QoQ at midpoint), gross margin in the range of 51.5%-53.5%, and operating margin in the range of 38%-40%. The gross margin dilution resulting from the N3 ramp-up would be 2-3 percentage points in Q3 2023 and 3-4 percentage points in Q4 2023. This impact would persist throughout the entire year of 2024, affecting the overall gross margin by 3-4 percentage points. Notably, this dilution is higher than the 2-3 percentage points gross margin dilution experienced during the N5’s second year of mass production in 2021.
- 2023revenue guidance revised down but expected:TSMC revised down the full-year revenue guidance to -10% YoY. The management sees weaker-than-expected macroeconomics in H2 2023 affecting the demand for all applications except for AI.
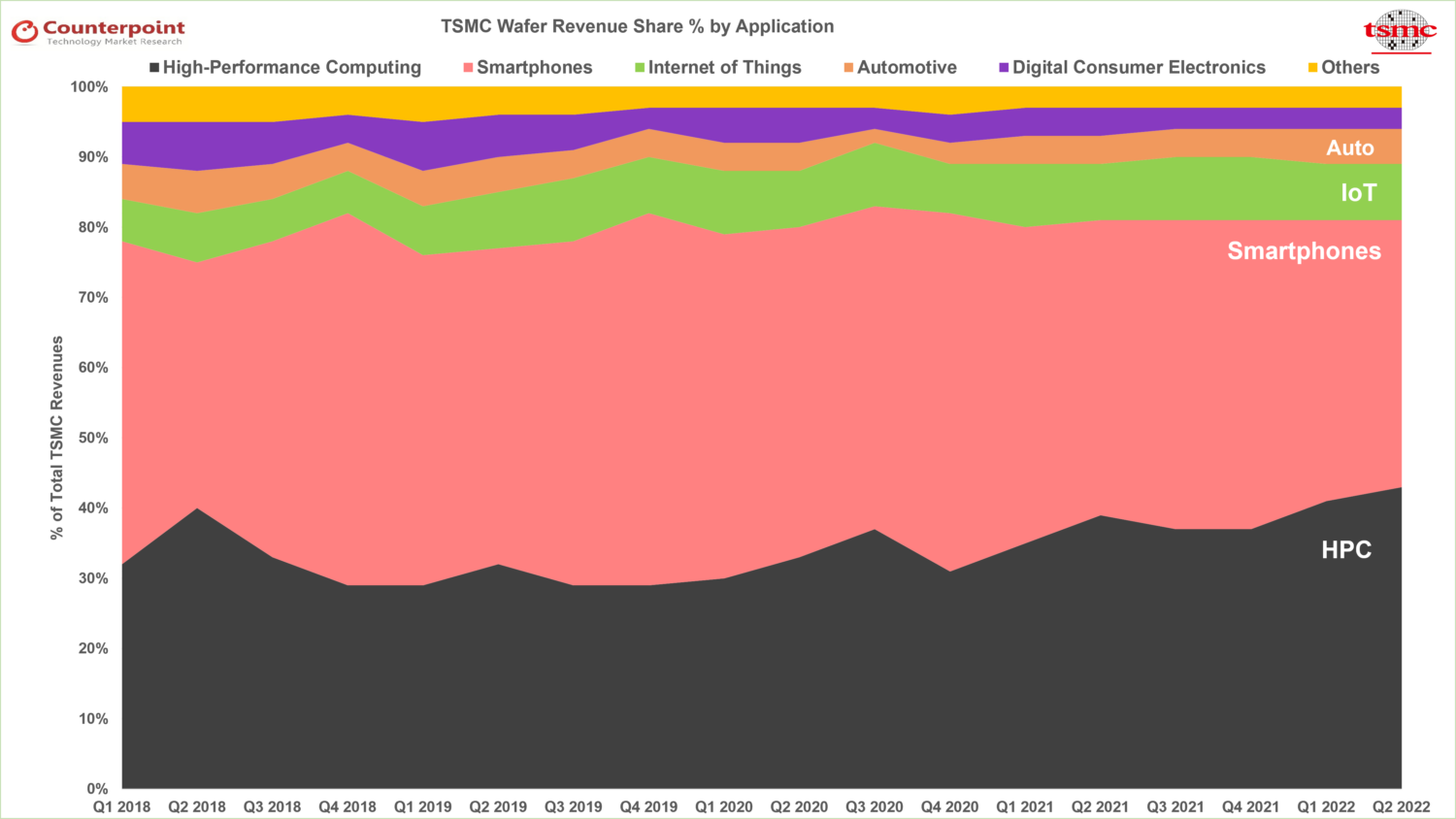
- Strong AIdemand, 50% revenue CAGR forecast:AI revenue currently makes up 6% of TSMC’s total revenue. The company anticipates a remarkable compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of nearly 50% from 2022 to 2027 in the AI sector. As a result of this significant growth, the AI revenue percentage share in TSMC’s total revenue is projected to reach the low teens by 2027.
- CoWoScapacity expected to double by 2024 end:TSMC is experiencing strong demand in the AI sector, with sufficient capacity for the front-end part but facing challenges in advanced packaging, particularly CoWoS.It is working with customers to meet demand in the short term while rapidly increasing capacity which it expects to double by the end of 2024, easing the current tightness.


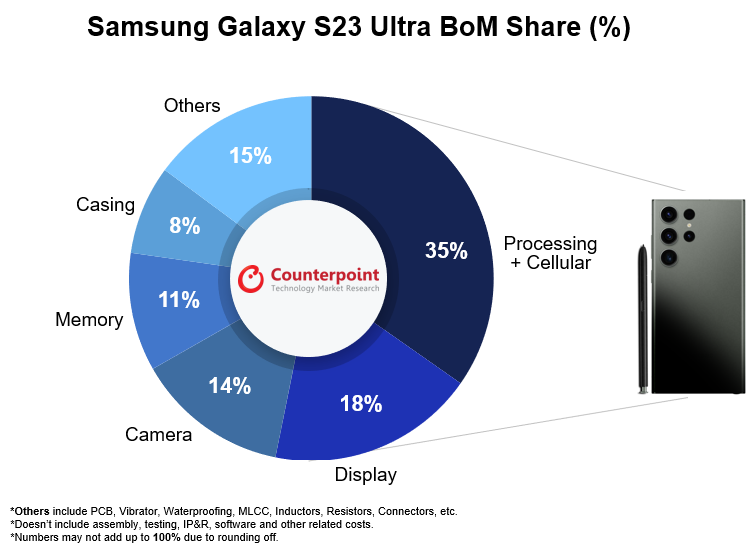
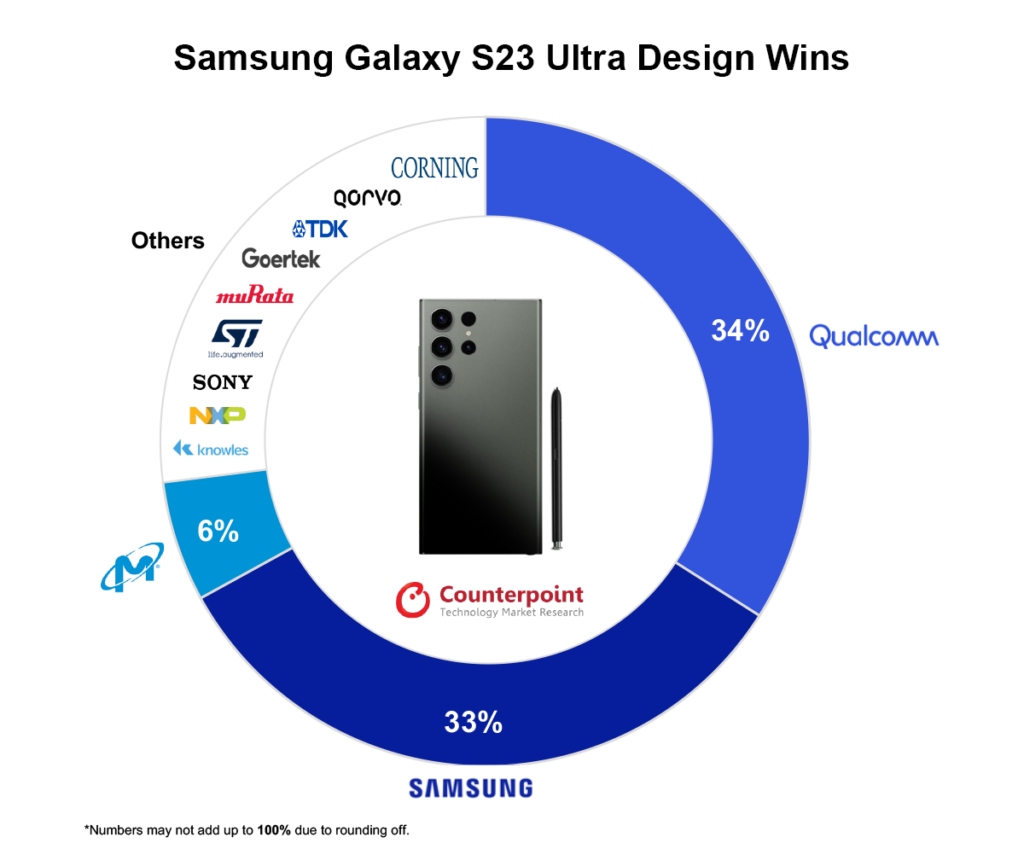





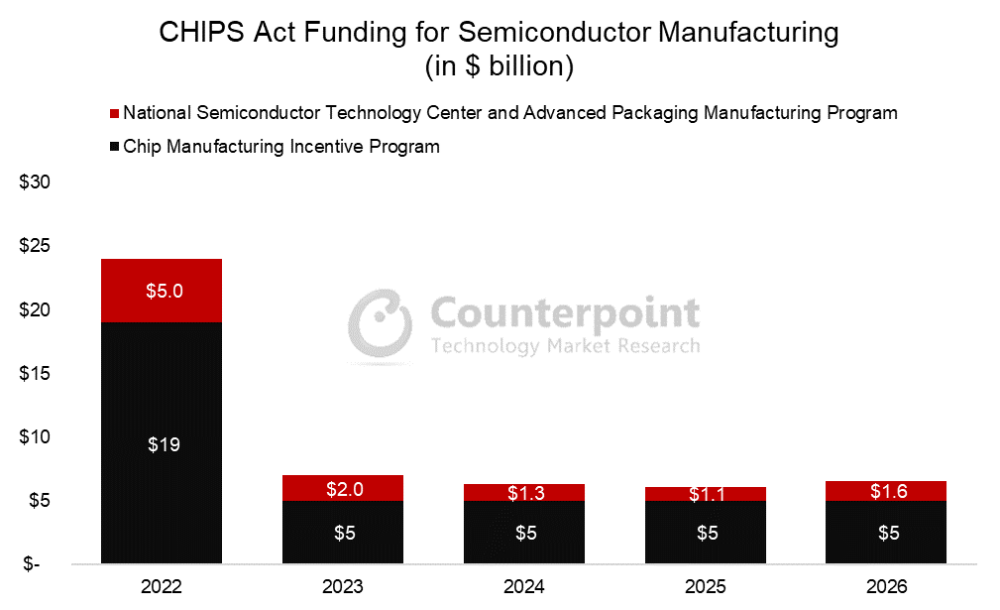
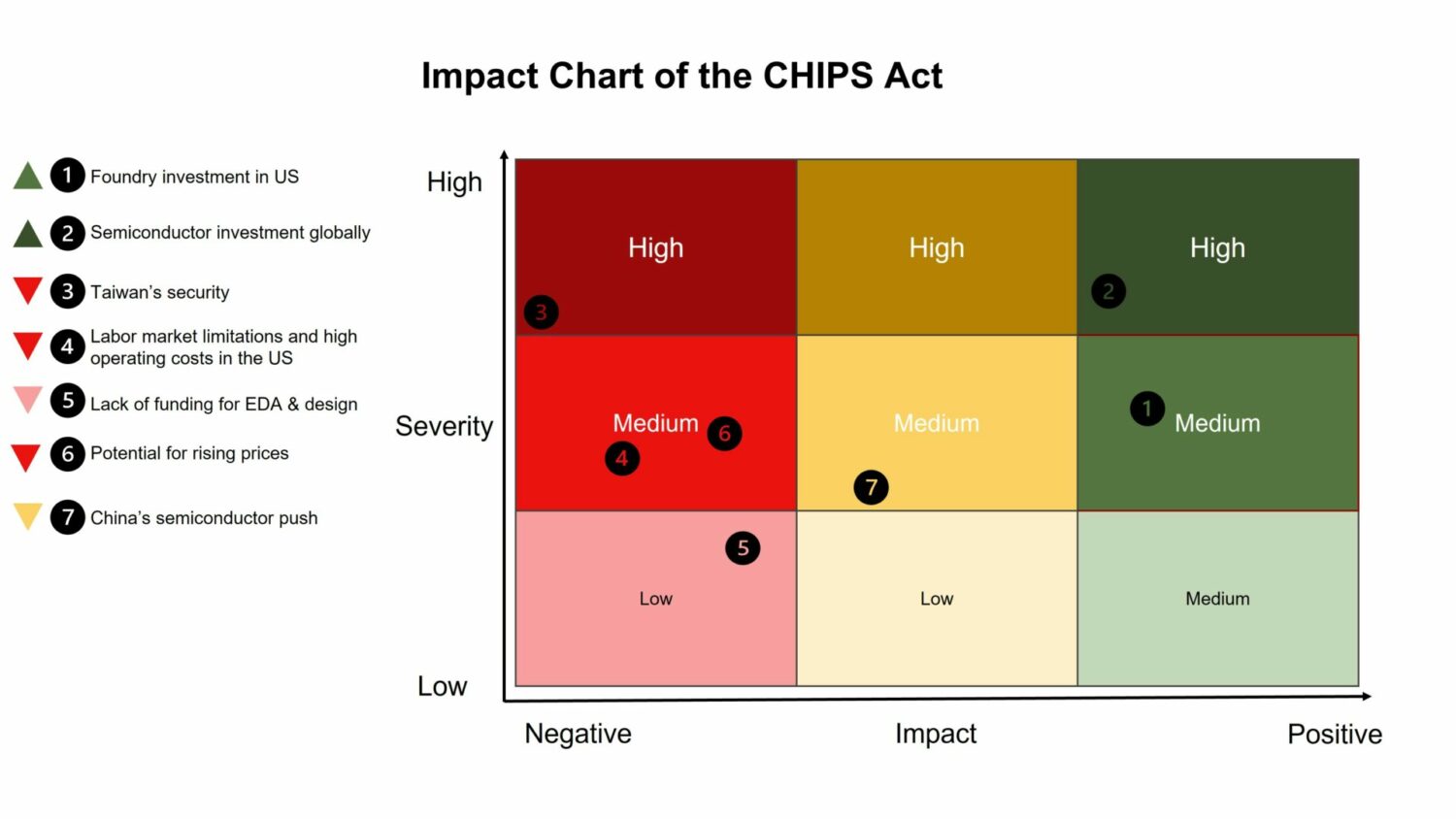 While flawed, the CHIPS Act is a major stepping stone to creating secure, resilient supply chains that will insulate the country from many outside shocks. This is a step in the right direction, but more must be done if the country wants to win the semiconductor manufacturing marathon and avoid fizzling out after the starting sprint.
While flawed, the CHIPS Act is a major stepping stone to creating secure, resilient supply chains that will insulate the country from many outside shocks. This is a step in the right direction, but more must be done if the country wants to win the semiconductor manufacturing marathon and avoid fizzling out after the starting sprint.







 TSMC’s major capital spending items in 2022 include:
TSMC’s major capital spending items in 2022 include: